Enterprise resource planning
What is ERP?
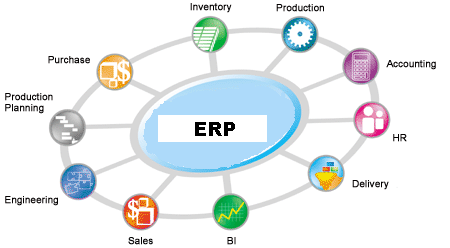
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is business process management software that allows an organization to use a system of integrated applications to manage the business and automate back office functions. ERP software integrates all facets of an operation, including product planning, development, manufacturing processes, sales and marketing.
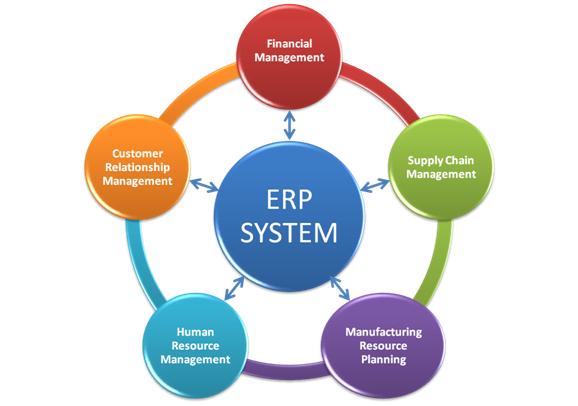
Below are some well know ERP modules which all together or independently act in the better decision making, planning and management.
- Sales
- Procurement
- CRM
- Supply chain management
- Manage human resources and payroll
Why ERP?
With an organization without ERP and many kind of software's which barley interact with each other has a serious impact on the organization management and planning, it provides quite a problem for concurrent management and planning across different functional departments which furthers seriously undermines the management and decision taking capability of the organization.
With ERP Information flows constantly and allows you to follow a client's processes at any moment, no matter which part of the process they are going through. With centralized database which allows you to have a close watch over the activities preventing possible abuse.
A powerfully ERP system enables interactions of various arms of organization like marketing, products processes, sales, quality control, supply lines, inventory and many other areas and it can be in a single database. This will eliminate the loss of data and retyping errors. It seamlessly integrates all departments and functions across a company into a single system that all those different department's needs.
An ERP system automates business processes by placing them into a useful format that is custom, standardized and common for the whole organization. This information can be shared between the suppliers and customers
Some of the advantages of the ERP
- Distribution process management
- Services knowledge base
- Improve accuracy of financial data
- Facilitate better project planning
- Automate employee life-cycle
- Standardize critical business procedures
- Reduce redundant tasks
- Assess business needs
- Accounting and financial applications
- Lower purchasing costs